Chapter 1 (Motion)
Motion:
If anybody changing its position with respect to time, then the body is said to be in
motion.
Or
A body is said to be in motion if it changes its position continuously with respect
to a stationary object taken as a reference point.
For example:
Let us consider two points A and B is far apart with each other, an object starts
changing its position from A to B with time then the object is said to be motion.

Distance:
The total length of the path travels by a body.
Example:
In the given image, Both of the figures represent the length of the path from A to B.
And both are the Distance. It is denoted by “s“, and it’s SI unit is m.
Displacement:
The minimum distance between the starting point and the ending point is known as
Displacement. It is also denoted by “s“, and it’s SI unit is m.
Example:
In the above image, the first figure represents the Displacement. And the second
one represents the Distance.
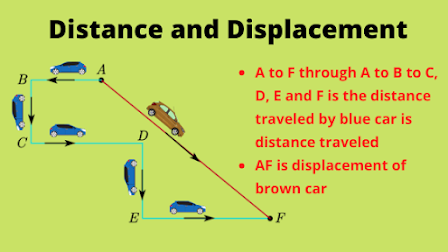
One more Image related to Distance and Displacement.
Difference Between Distance And Displacement:
Uniform Motion:
If anybody travels the equal distance in an equal interval of time, then its motion is
said to be a uniform motion.
For Example:
Non-Uniform Motion:
If anybody travels the unequal distance in an unequal interval of time, then it’s
motion is known as Non-Uniform Motion.
For Example:
In the given figure, a car travels the irregular distance in the unequal interval of time.
Speed:
The rate of change of distance w.r.t (with respect to) time is known as speed. Speed
is denoted by “v“. Its SI unit is m/s.
The formula for the calculation of Speed(u) is given below ;
u=s/t
Average Speed:
It is defined as the total distance traveled by a body divided by the total time taken.
Its unit is m/s, and it is also represented by “v“.
The formula for the calculation of Average Speed(u)
Average Speed(u) = Total distance / Total time taken
Uniform Speed(or constant speed):
If anybody travels the equal distance in equal interval of time, its speed is known as
Uniform Speed.
Velocity:
The rate of change of displacement w.r.t to time is called displacement. It is denoted
by “v“, and it’s SI unit is m/s.
The formula for the calculation of Velocity(v) is given below;
Velocity(v)=Displacement(s) / Time Taken(t)
Initial Velocity:
When the observer starts his observation, then the velocity is known as
Initial Velocity. It is denoted by “u”.
Final Velocity:
When the observer ends his observation, the velocity is known as Final Velocity.
It is denoted by “v”.
Note:- m/s is the SI unit of both initial and final velocity.
Thanku so much sir for ur all videos.
ReplyDeleteYou worked hard for the betterment of students